File Obfuscator User Manual
Table of Contents
- Overview
- How It Works
- Features
- Usage Guide
- API Reference
- Security Features
- Troubleshooting
- Examples
- Best Practices
Overview
File Obfuscation is a feature in iotsploit client that combines steganography and encryption to hide files within images. It provides a secure way to conceal sensitive documents, messages, or any digital content within seemingly innocent image files, effectively bypassing regulatory monitoring and content filtering systems.
Location: In iotsploit client, the File Obfuscation tool is available in the Toolkit section under the “File Obfuscation” card.
What is Steganography?
Steganography is the practice of concealing information within other non-secret data or a physical object. In our case, we hide files within images in a way that is invisible to the human eye and difficult to detect without the proper tools.
What is File Obfuscation?
File obfuscation involves making files unreadable or unrecognizable to unauthorized users while maintaining their original functionality for authorized users.
Regulatory Bypass Benefits
By embedding files within images, this tool provides an effective method to bypass regulatory monitoring systems:
- Content Filtering Evasion: Image files are typically not subject to the same content scanning as document files
- Network Monitoring Avoidance: Image transfers often pass through monitoring systems without triggering alerts
- Platform Restrictions Bypass: Many platforms allow image sharing while restricting document uploads
- Stealth Communication: Enables secure file transmission that appears as normal image sharing
How It Works
The File Obfuscator uses a multi-layered approach to securely hide files:
1. Encryption Layer
- AES-256 Encryption: Industry-standard encryption algorithm
- Salt Generation: Random 16-byte salt for each operation
- IV (Initialization Vector): Random 16-byte IV for each encryption
- Key Derivation: PBKDF2-like key derivation using HMAC-SHA256
2. Compression Layer
- ZIP Archive: Compresses encrypted data for efficient storage
- Metadata Storage: Stores file information and encryption parameters
- File Organization: Structured archive with encrypted file and metadata
3. Steganography Layer
- Image Carrier: Uses your selected image as the carrier
- Data Appending: Appends the encrypted archive to the image data
- Seamless Integration: The image remains visually identical
Features
🔒 Advanced Security
- AES-256 encryption with CBC mode
- Unique salt and IV for each operation
- Strong password-based key derivation
- Tamper-resistant metadata storage
🖼️ Image Compatibility
- Supports all common image formats
- Maintains original image quality
- No visible changes to the carrier image
- Efficient data embedding
📦 Smart Compression
- ZIP compression for optimal storage
- Metadata preservation
- Fast compression and decompression
- Cross-platform compatibility
🔑 Password Protection
- User-defined passwords
- Salt-based key derivation
- No password storage in the system
- Secure key generation
🚫 Regulatory Bypass
- Bypasses content filtering systems
- Evades network monitoring
- Overcomes platform restrictions
- Enables stealth file transmission
Usage Guide
How to Find the File Obfuscator Tool
The File Obfuscator tool is located in the Toolkit section of your Flutter application:
-
Launch the Application
- Open your Flutter application
- Look for the main navigation menu
-
Navigate to Toolkit
- Find and click on the “Toolkit” menu item
- This will take you to the toolkit overview page
-
Locate File Obfuscation
- Look for the “File Obfuscation” card
- It displays the description: “Hide files in images using steganography and encryption”
- The card has a distinctive icon representing file obfuscation
-
Access the Tool
- Click on the “File Obfuscation” card
- This will open the File Obfuscator interface
Prerequisites
- Flutter GUI application with the File Obfuscator tool
- Image file to use as carrier
- File to hide
- Strong password for encryption
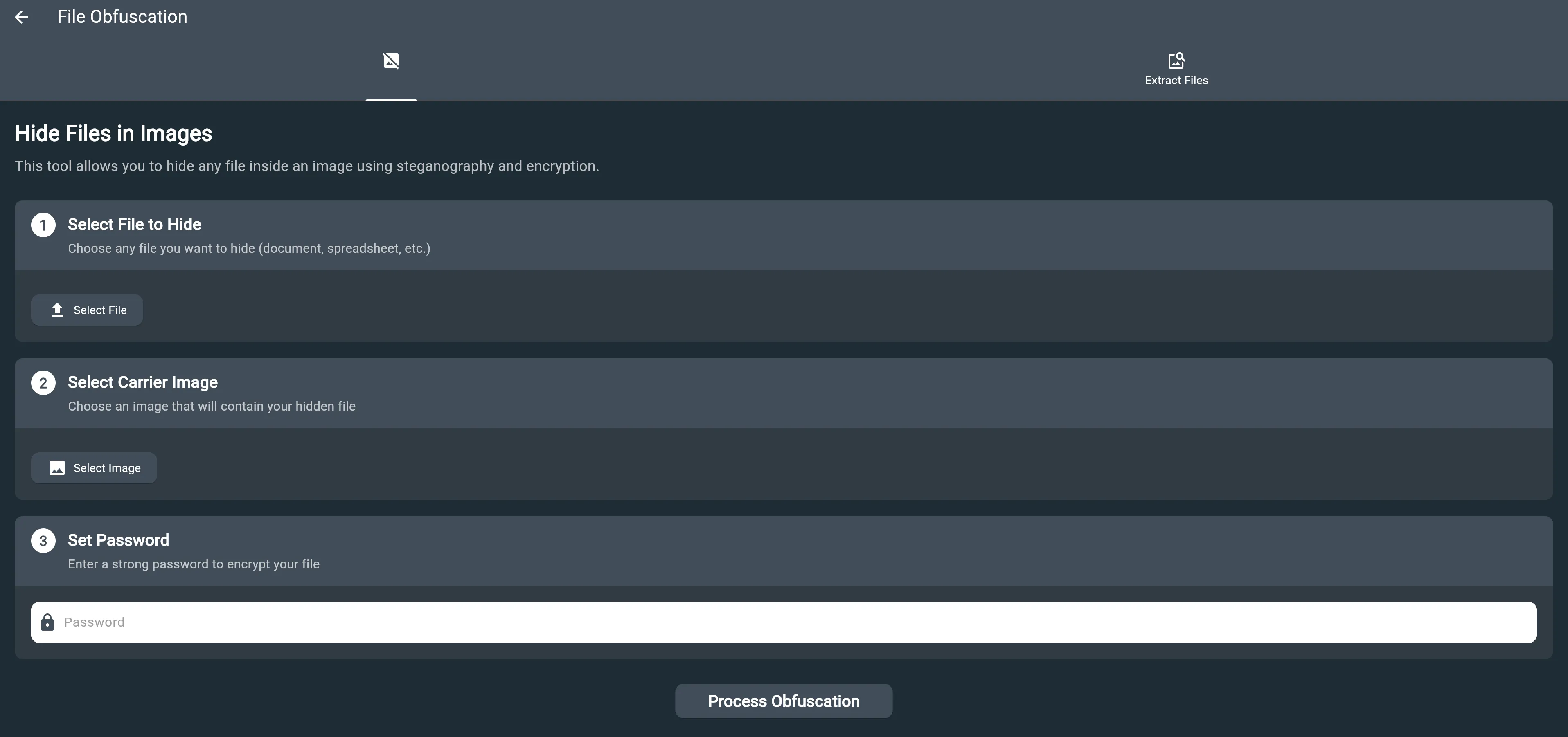
Step 1: Hiding a File
-
Open the File Obfuscator Tool
- Launch your Flutter application
- Navigate to the Toolkit section
- Click on the “File Obfuscation” card
- Select “Hide File” option from the tool interface
-
Select Your Files
- Choose the file you want to hide
- Select an image to use as the carrier
- Enter a strong password for encryption
-
Configure Settings
- Verify the file and image selections
- Review the encryption settings
- Confirm the output location
-
Execute the Process
- Click “Hide File” button
- Wait for the process to complete
- Save the resulting obfuscated image
Step 2: Extracting a File
-
Open the Extraction Tool
- Navigate to the Toolkit section
- Click on the “File Obfuscation” card
- Select “Extract File” option from the tool interface
-
Load the Obfuscated Image
- Choose the image containing hidden data
- Enter the password used for encryption
-
Extract the File
- Click “Extract File” button
- Wait for the decryption process
- Choose where to save the extracted file
-
Verify the Result
- Check that the file was extracted correctly
- Verify the original filename is preserved
- Ensure file integrity is maintained
⚠️ Important Warning: If the obfuscated image was compressed or modified by chat applications (WeChat, WhatsApp, Telegram, etc.), file extraction may fail. Always use the original obfuscated image file for extraction.
Tool Features
File Hiding Function
The File Obfuscator tool provides a comprehensive file hiding capability:
What it does:
- Encrypts your selected file using AES-256 encryption
- Generates unique security parameters for each operation
- Compresses the encrypted data for efficient storage
- Embeds the data seamlessly within your chosen image
- Preserves the original image quality and appearance
Input Requirements:
- File to hide (any type and size)
- Carrier image (JPEG, PNG, GIF, etc.)
- Strong password for encryption
- Output location for the result
Output:
- An image file that looks identical to the original
- Contains your hidden file securely encrypted
- Ready for storage, sharing, or transmission
File Extraction Function
The tool also provides secure file extraction:
What it does:
- Detects hidden data within obfuscated images
- Validates the image integrity
- Decrypts the hidden file using your password
- Restores the original file with its original name
- Maintains file integrity and metadata
Input Requirements:
- Image file containing hidden data
- Correct password used during encryption
- Destination folder for extracted file
Output:
- Original file restored exactly as it was
- Preserved filename and file structure
- Ready for normal use
⚠️ Critical Requirement: The image file must be exactly the same as when it was created. Any compression, resizing, or modification will prevent successful extraction.
Security Features
Encryption Details
- Algorithm: AES-256 in CBC mode
- Key Size: 256 bits (32 bytes)
- Salt: 16 random bytes per operation
- IV: 16 random bytes per encryption
- Key Derivation: HMAC-SHA256 with salt
Security Benefits
- Confidentiality: Files are encrypted and unreadable without the password
- Integrity: Tampering with the image will corrupt the hidden data
- Authentication: Only users with the correct password can access files
- Non-repudiation: Each operation uses unique cryptographic parameters
Threat Protection
- Brute Force: Strong encryption makes password guessing extremely difficult
- Known Plaintext: Salt and IV prevent pattern analysis
- Side Channel: No timing or memory leaks in the implementation
- Data Recovery: Corrupted images cannot be used to recover hidden files
- Regulatory Detection: Steganographic techniques make detection extremely difficult
- Content Analysis: Bypasses automated content scanning and filtering systems
Troubleshooting
Common Issues and Solutions
1. “Failed to create ZIP archive”
Cause: Memory issues or corrupted input data Solution:
- Ensure sufficient memory is available
- Verify input file integrity
- Check file size limits
2. “No hidden file found in the image”
Cause: Image doesn’t contain hidden data or is corrupted Solution:
- Verify the image contains hidden data
- Check if the image was modified after hiding
- Ensure the correct image file is being used
3. “Metadata file not found in the hidden data”
Cause: Corrupted or incomplete hidden data Solution:
- Verify the image wasn’t truncated
- Check for file corruption
- Ensure the complete image is loaded
4. “Error extracting file”
Cause: Incorrect password or corrupted data Solution:
- Verify the password is correct
- Check for typos in the password
- Ensure the image wasn’t modified
5. “File extraction failed after chat transmission”
Cause: Image compression or modification by chat applications Solution:
- Always use the original obfuscated image file
- Avoid sharing through chat apps that compress images
- Use direct file transfer methods (email, cloud storage, USB)
- Verify image file size hasn’t changed after transmission
Performance Tips
- Use appropriate image sizes for your hidden files
- Consider file compression before hiding
- Use strong, memorable passwords
- Keep backups of original files
Usage Scenarios
Scenario 1: Hiding Personal Documents
Use Case: You want to hide important personal documents like contracts, certificates, or financial statements within an innocent-looking photo.
Process:
- Select your sensitive document file
- Choose a family photo or vacation picture as the carrier
- Set a strong, memorable password
- Hide the file and save the result
- Store the obfuscated image safely
Benefits: Your documents are now hidden in plain sight, appearing as just another photo in your collection.
Scenario 2: Secure File Sharing
Use Case: You need to share confidential files with colleagues or clients through email or cloud storage.
Process:
- Hide the confidential file in a professional image
- Share the image file through your preferred channel
- Provide the password separately via secure communication
- Recipients use the tool to extract the hidden file
Benefits: Files can be shared through any channel without revealing their sensitive nature.
Scenario 2.5: Regulatory Bypass Communication
Use Case: You need to transmit sensitive information in environments with strict content monitoring or restrictions.
Process:
- Hide sensitive documents within ordinary images
- Share images through standard communication channels
- Bypass content filtering and monitoring systems
- Maintain secure access through password protection
Benefits: Effective bypass of regulatory monitoring while maintaining security and confidentiality.
Scenario 3: Backup and Archiving
Use Case: You want to create secure backups of important files that won’t attract attention.
Process:
- Hide multiple important files in a single image
- Use a memorable image as the carrier
- Store the obfuscated image in multiple locations
- Access your files whenever needed with the password
Benefits: Secure backups that blend in with your regular photo collection.
Scenario 4: Travel and Mobile Use
Use Case: You’re traveling and want to carry important documents without physical copies.
Process:
- Hide important documents in travel photos
- Store the images on your phone or cloud
- Access documents anywhere using the mobile app
- No need to carry physical documents
Benefits: Digital document storage that’s both secure and inconspicuous.
Best Practices
Security Best Practices
-
Use Strong Passwords
- Minimum 12 characters
- Mix of uppercase, lowercase, numbers, and symbols
- Avoid common words or patterns
- Use unique passwords for different purposes
-
Choose Appropriate Carrier Images
- Use high-quality images
- Avoid heavily compressed formats
- Consider image size vs. hidden file size
- Use images that won’t attract suspicion
-
File Management
- Keep original files as backups
- Store passwords securely
- Don’t share obfuscated images publicly
- Regularly update passwords
-
Image Transmission Safety
- Never share through chat apps that compress images (WeChat, WhatsApp, Telegram)
- Use direct file transfer methods (email, cloud storage, USB drives)
- Verify file integrity after transmission
- Keep the original obfuscated image for extraction
Performance Best Practices
-
File Size Optimization
- Consider file size before hiding (larger files take longer to process)
- Use appropriate image formats (JPEG for photos, PNG for graphics)
- Balance image quality vs. processing speed
- Be patient with large files during processing
-
Tool Usage
- Don’t interrupt the process while it’s running
- Close other applications to free up system resources
- Ensure stable internet connection if using cloud features
- Keep the application updated for best performance
Operational Best Practices
-
Testing and Verification
- Start with small files to test the tool
- Always verify extraction works before deleting original files
- Test with different image formats to ensure compatibility
- Practice password recovery to avoid data loss
-
File Organization
- Keep a secure record of which images contain hidden files
- Store passwords securely (not in the same location as the images)
- Maintain a simple inventory of hidden files
- Use descriptive names for obfuscated images
Support and Contact
For technical support or questions about the File Obfuscator:
- Documentation: Refer to this manual
- Code Examples: Check the examples section
- Troubleshooting: Use the troubleshooting guide
- Security: Review security best practices